
Maternal nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting both maternal health and optimal foetal development. During pregnancy, the physiological demands of the body increase significantly, necessitating adjustments in dietary intake to meet the nutritional requirements of both mother and child.1 Inadequate maternal nutrition has been associated with a higher risk of complications, including low birth weight and small for gestational age; conversely, excessive energy intake or poor dietary quality may contribute to gestational diabetes, hypertension, and other metabolic disorders.1
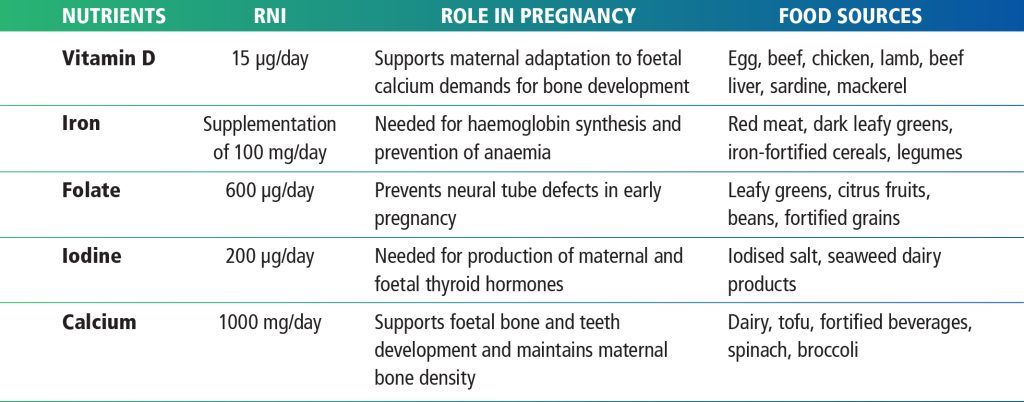
Meeting the nutrient requirements in accordance with the Ministry of Health (MOH) Malaysia’s Recommended Nutrient Intakes (RNI) is essential to ensure the health of both mother and child. Table 1 shows the RNI of a few key micronutrients that is essential for pregnant women and its role during pregnancy and its food sources.
Table 1: RNI of key nutrients, its role in pregnancy and food sources.1-3
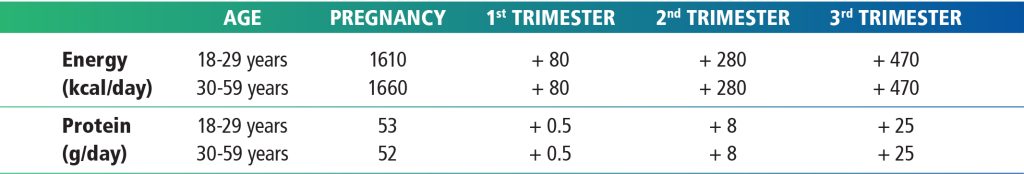
Ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients is crucial, but it is equally important to adjust overall energy and protein consumption to meet the physiological demands of pregnancy.2 The traditional concept of "eating for two" should not be interpreted as doubling caloric intake. Instead, pregnant women should aim for a balanced and varied diet that provides enough energy and protein to support the stages of foetal growth and maternal changes. The additional energy and protein intake that is required during pregnancy according to the Maternal Dietary Guidelines for Malaysia (MDGM), 2023 is as outlined in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommendations of additional energy and protein needs for pregnant women in Malaysia2
To support these increased needs while staying within recommended energy limits, pregnant women are encouraged to consume 1 to 3 healthy snacks per day and a variety of foods from all food groups.2 This can be effectively guided by the Malaysian Healthy Plate (Figure 1), which recommends that half of the plate consist of fruits and vegetables, one-quarter with high-quality carbohydrates, and one-quarter with protein sources such as meat, poultry, fish, legumes, or eggs. Adhering to the Malaysian Healthy Plate supports adequate intake of essential nutrients in recommended portions.2

Figure 1: Malaysian Healthy Plate
Taken from National Coordinating Committee on Food and Nutrition. MOH. 2023.
In conclusion, a balanced and nutrient-rich diet consisting of ample fruits and vegetables, high-quality carbohydrates, a variety of protein sources, and polyunsaturated fats is essential during pregnancy. By aligning dietary choices with guidelines and recommendations from the MOH, pregnant women can better support the health of their own and of their child.
Like what you read?
Let us know what you think.
Contact us for any comments and enquiries:
E: info@mediconnexionsconsulting.com
T: +603 7832 0188
Mediconnexions Consulting Sdn. Bhd. offers a wide range of integrated marketing and communications services related to the medical, pharmaceutical and nutritional sciences.
Visit our website at www.mediconnexionsconsulting.com
Medical webinar organiser Malaysia, creative agency for medical Malaysia, medical conference organiser, medical digital marketing agency, medical marketing agency, medical writer Malaysia, medical writer.
References